1.2.1 Closed Loop Systems
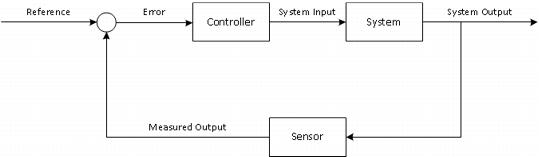
Closed loop control systems are those that provide feedback of the actual state of the system and compare it to the desired state of the system in order to adjust the system.
1.2.1.1. Control Theory
The closed loop control system is a system where the actual behavior of the system is sensed and then fed back to the controller and mixed with the reference or desired state of the system to adjust the system to its desired state. The objective of the control system is to calculate solutions for the proper corrective action to the system so that it can hold the set point (reference) and not oscillate around it.
Figure 1. Closed Loop Control System
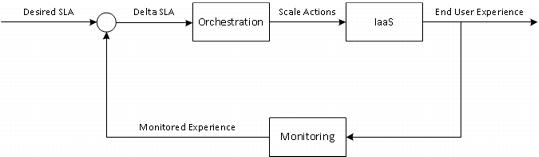
1.2.1.2. Closed Loop Dynamic IaaS
When a scale out triggering event occurs, the input parameter that triggers the event is monitored around its set point. The system increases and decreases capacity on demand to stay as close as possible to the set point for the triggering parameter.
With closed loop systems, you can evaluate the system near the set point using a PID control algorithm or similar control scheme. A simpler approach, such as hysteresis, can be very effective and can be implemented with less complexity and tuning.
Hysteresis is the dependence of a system not only on its current state but also on its past state. For example, a thermostat controlling a heater may turn the heater on when the temperature drops below x degrees, but not turn it off until the temperature rises above y degrees.
An example of a closed loop dynamic IaaS system is one in which the infrastructure is constantly monitoring the end-user experience. When an end-user experience measure drops below a desired threshold, for example, transactions taking > n milliseconds, the controller scales out the environment to compensate. The experience is checked with the new resources, and if it still is below the desired state, it continues to scale out the service. When the transaction time drops below the desired n milliseconds, the controller scales back the environment to reduce the resources consumed and continues to monitor whether the user experience is within the acceptable range.
Figure 2. Closed Loop Dynamic IaaS