5.2.3.1. Implementation
As an example, create Storage DRS clusters in the vSphere domain. In this scenario, there are two datastores (bronze1, bronze2) backed by SATA storage, and two datastores (gold1, gold2) backed by FC storage. There are also other datastores but they are not part of this implementation example.
To create Storage DRS clusters in the vSphere domain
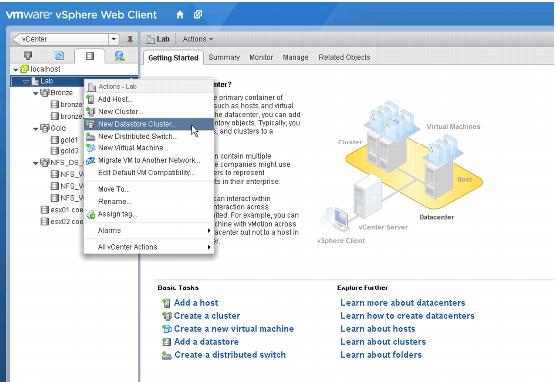
1. Create a new datastore cluster.
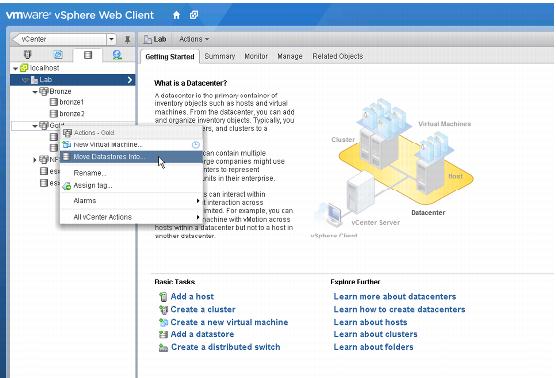
2. Move existing datastores into the cluster.
3. For each of the four datastores, click the datastore and assign a storage capability.
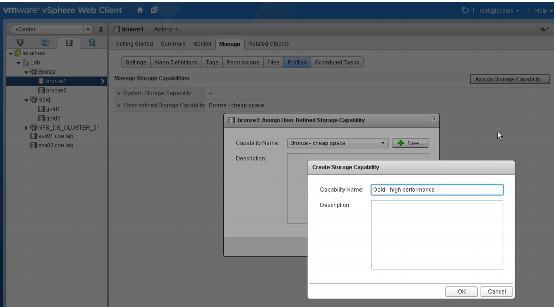
4. If you have not defined a storage capability, create a new one as illustrated in this screenshot. Assign the storage capability. In this example, the storage capabilities are named “Bronze – cheap space” and “Gold – high performance”.
Note: It is important that all datastores in the same cluster are assigned the same homogenous Storage Capability. Otherwise, the proper storage profile does not appear as available in the vCloud Director interface.
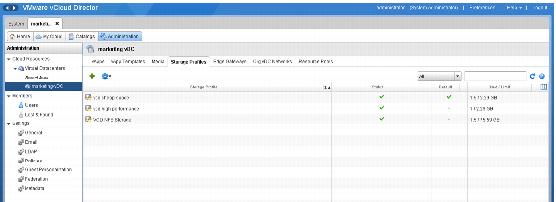
5. Create VM Storage Profiles. Each VM Storage Profile can have one or more storage capabilities. This example shows two VM Storage Profiles (“vcd cheap space” and “vcd high performance”).
The “Bronze – cheap space” and the “Gold – high performance” storage capabilities are assigned to these VM Storage Profiles, respectively.
The following screenshot shows how the “vcd – high performance” VM Storage Profile has been configured.
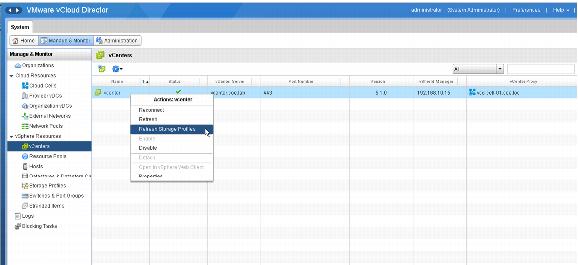
6. Switch to the vCloud Director management portal and configure these VM Storage Profiles in the provider virtual datacenter.
Additional VM Storage Profiles, if available, are displayed in the Add Storage Profile window.
If a configured VM Storage Profile is not displayed in the list, make sure that the proper storage capability has been consistently configured for each datastore in the datastore cluster. Although vSphere marks a cluster as Incompatible when you select a particular VM Storage Profile in the VM deployment wizard, vCloud Director does not show anything in the list unless it is Compatible.
7. A configured VM Storage profile also might not be displayed because vCloud Director has not yet synced with the vSphere platform. This sync happens every five minutes but you can force a re-sync.
8. Create an organization virtual datacenter for the organization.
Note: This organization virtual datacenter was created for the marketing organization. There is a default Storage Profile defined for the organization virtual datacenter. This is the default selection for virtual machines when vApp Authors and vApp Users deploy virtual machines. Being able to change the default settings of a storage profile is a privilege that you can use when defining user roles. By default, this privilege is assigned to organization administrators.
When a vApp author deploys a two-tier vApp that requires different storage characteristics for each virtual machine in the vApp, the user can choose different storage profiles for each of the virtual machines. This is shown in the following figure.
Figure 35. vApp Deployment Storage Profile
These virtual machines reside on a cluster of datastores managed by vSphere, thus leveraging all of the advantages that the underlying platform provides.