Secure Certificates
To provide security for a VMware vCloud Director-based cloud service, VMware requires the implementation of certificates and key management for secure access and authentication to the vCloud Director server during its installation.
vCloud Director performs symmetric encryption to protect sensitive data from eavesdroppers and unwanted guests and public-key encryption to exchange keys securely over an insecure transport, as well as supporting certificates and their digital signatures to establish a trust relationship. This makes it possible to create a secure protocol and channel between the vCloud Director service and end-tenant that functions over an insecure connection without any previous interaction between the parties. This enables secure data transmission in a shared, multitenant environment, such that the intended recipient can be assured communication with the intended receiver.
Secure Certificates Example
Deployment Models: private, public, hybrid
Using the SSL/TLS protocol in the vCloud environment provides secure communication between the end-tenant (client) and vCloud Director cell (server). Providing this secure communication presents us with the following main objectives:
 Confidentiality and
Confidentiality and privacy of communication.

Message
integrity and hashing.

Authentication.
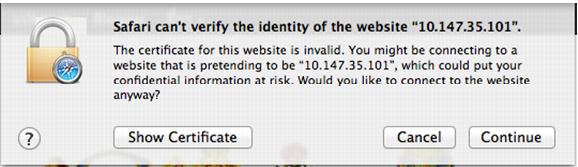
While using your web browser you might have seen the warning message that “This site’s identity cannot be trusted," In this case, either the certificate has expired, or it was issued by a certificate authority that you do not trust. It is the primary role of SSL/TLS to provide confidentiality and privacy of the communication, and to prevent MITM (man-in-the-middle) attacks, side channel attacks, and tax intended to compromise your privacy and security.
Figure 50. Example Error Message
Message Integrity and Hashing is the ability to guarantee that the data’s content has not been modified during the protocol exchange and transmission.
Using certificates for authentication is the process of confirming an identity. In the context of network interactions, authentication is the confident identification of one party by another party. Certificates are one way of supporting authentication.
Certificates or digital certificates are collections of data that uniquely identify or verify an individual, company, or other entity on the Internet. Certificates also enable secure, confidential communication between two entities. In the context of vCloud Director, server certificates are used to establish secure sessions between the cell server and clients through secure sockets layer (SSL) and Transport Layer (TLS) technology.
Here we see a website that has been secured with an SSL certificate and that is denoted and displayed with a URL You can also see a padlock symbol on the top right far corner of your browser (in this example).
Types of SSL Certificates:

Self-Signed cert
– Generated for internal purposes and is not issued by a CA.

Domain Signed cert:
 An entry level SSL Certificate and can be issued quickly.
An entry level SSL Certificate and can be issued quickly. 
The only check performed is to
verify that the applicant owns the domain where they plan to use the certificate.

No additional checks are done to
confirm that the owner of the domain is a valid business entity.

Fully authenticated SSL Certificate:
 First step to true online security and confidence building.
First step to true online security and confidence building. 
Takes slightly longer to issue
because these certificates are only granted
after the organization passes a number of validation procedures and checks to confirm the existence of the business, the ownership of the domain, and the user’s authority to apply for the certificate.

SGC
(Server-Gated-Cryptography)-enabled SSL Certificate
– Used for old browsers
or clients
that do not support 128/256 bit encryption.

Wildcard certificate
– Allow full SSL security to any host in domain.
 SAN (Subject Alternative Name) SSL Certificate –
SAN (Subject Alternative Name) SSL Certificate – Allow more than one domain to be added to a single SSL Certificate.

Code Signing Certificate
– Specifically designed to make sure that the software you have downloaded was not tampered with while en route.
 Extended Validation (EV) SSL Certificates –
Extended Validation (EV) SSL Certificates – Offers the highest industry standard for authentication and provide the best level of customer trust available.
Whether you are a private, hybrid or public vCloud provider, VMware recommends implementing SSL Certificates from a Trusted CA.
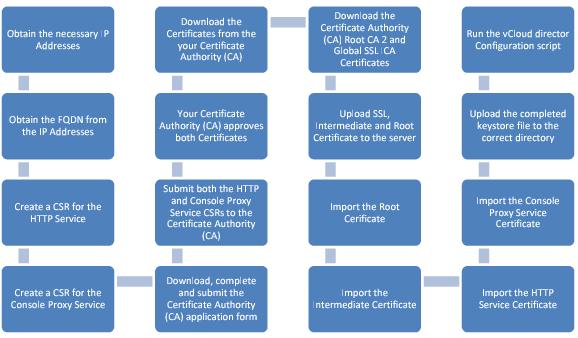
The following process flow outlines all of the steps that involve requesting, configuring, obtaining and installing an SSL certificate from a CA who can be used as Certificate Authority for vCloud Director.
Figure 51. Requesting, Configuring, Obtaining and Installing an SSL Certificate from a CA

When using SSL Certificates it is important to understand and evaluate
the different types of SSL Certificates that are available
and use one that matches your requirements.

In a production environment,
do not configure vCloud Director to use self-signed certificates. This
is an insecure practice. Self-signed certificates are certificates that are digitally signed by the private key corresponding to the public key included in the certificate. This is done in place of a CA signing the certificate. By self-signing a certificate, you are attesting that you are who you say you are. No trusted third-party
validation is involved.
Self-signed certificates do not have a valid chain of signatures leading to a trusted root certificate. They provide a weaker form of security because,
though you can verify such a certificate is internally consistent, anyone can create one, so by examining the certificate, you cannot know if it is safe to trust the issuer or the site from which the certificate is coming. Nevertheless, self-signed certificates are common. For example, vCenter installations use a self-signed certificate by default.

The server keystore should be considered highly sensitive
because a compromise of the server key allows impersonation of the server and/or access to the encrypted traffic. Java keystores provide a method of securely storing private keys and their associated certificates, protected by a password. vCloud Director only supports the JCEKS format for keystore files. (Other formats that Java supports include PKCS12 and JKS
. JKS is less secure and
not recommended).