8.1 Scenario #1 – Multi-Site Common User Interface
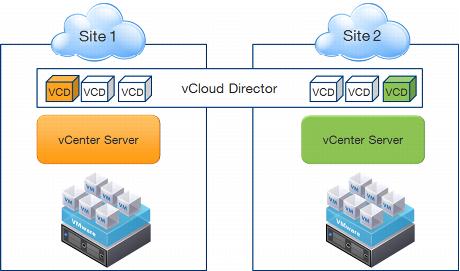
Scenario 1 shows a use case where one vCloud Director instance supports two locations. vCloud Director cells provide the web console and can be placed in either or in both locations. As illustrated in
Figure 44, one vCloud Director cell serves as the proxy for a vCenter Server in one of the sites.
Splitting the cells across sites add the potential for user console access to cross the sites unnecessarily. When a user accesses a virtual machine console in VCD, load-balanced VCD cells choose the best available cell to route the console connection. This connection might not be through a cell local to the requestor. Additional steps can be taken to minimize cross-site console access by using load balancer rules.
Figure 44. Two Sites with Local VCD Instances Managing Two Local vCenter Servers
The local vCenter Servers control resources local to each site. This might seem like a very logical infrastructure setup until you examine some of the user flows.
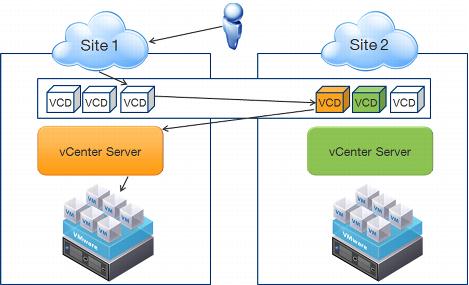
If a user comes in through site #1 and requests remote console access to a virtual machine in site #1, all traffic is not guaranteed to stay in site #1. This is because it is not possible to control which vCloud Director cell acts as the proxy for a particular vCenter Server. A user could initiate a session through a vCloud Director cell in site #1, which then communicates to the proxy for vCenter server #1 in site #2. That vCloud Director cell talks back to the vCenter server in site #1 to finish establishing the remote console connection to the local vSphere host
hosting the workload in site #1. Traffic flows through the vCloud Director cell that initiated the request in site #1. Figure 45 illustrates the flow of events.
Figure 45. Remote Console Flow
Another problem with this setup is controlling the vCloud Director cell that a user is terminated on based on virtual machine and site-specific data. It is nearly impossible to figure this out and provide that logic to a load balancer. In addition, a centralized vCloud Director database is needed to support all vCloud Director cells from both sites. This creates even more traffic on the link between the two sites because the message bus in vCloud Director uses the vCloud Director database for communication. Overall, this solution is less than optimal for most use cases, with the exception of cross-campus multi-site configurations where site-to-site communication will not overwhelm the network and where network availability is highly reliable.