5.9.1 Snapshot Architecture
A snapshot preserves the state and data of a virtual machine at a specific point in time.

The state includes the virtual machine’s power state (powered-on, powered-off, suspended).

The data includes all of the files that make up the virtual machine.
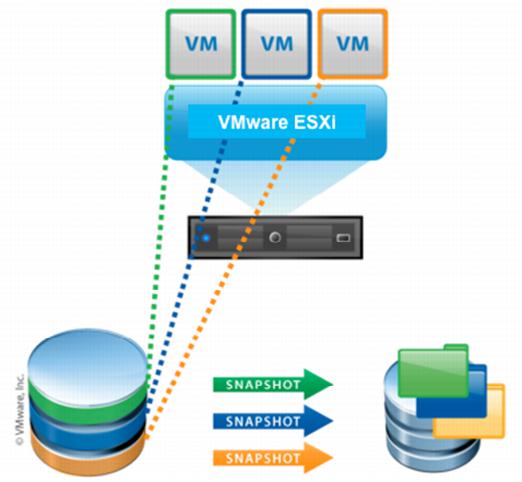
Snapshots work by creating delta copies (point-in-time) of the specified virtual machine files. The following figure provides a high level illustration of how this works.
Figure 33. Snapshot Processing
When a snapshot is created, it is comprised of the following files:

<vm>-<number>
.vmdk and <vm>-<number>-delta.vmdk.
 A collection of .vmdk and -delta.vmdk files for each virtual disk is connected to the virtual machine at the time of the snapshot. These files can be referred to as child disks, redo logs
A collection of .vmdk and -delta.vmdk files for each virtual disk is connected to the virtual machine at the time of the snapshot. These files can be referred to as child disks, redo logs,
or delta links. These child disks can later be considered parent disks for future child disks. From the original parent disk, each child constitutes a redo log
that points back from the present state of the virtual disk, one step at a time, to the original one. Note: The <number> value may not be consistent across all child disks from the same snapshot. The file names are chosen based on filename availability.

<vm>
.vmsd: The .vmsd file is a database of the virtual machine's snapshot information and the primary source of information for the snapshot manager. The file contains line entries that define the relationships between snapshots as well as the child disks for each snapshot.

<vm>Snapshot<number>
.vmsn: These files are the memory state at the time of the snapshot.